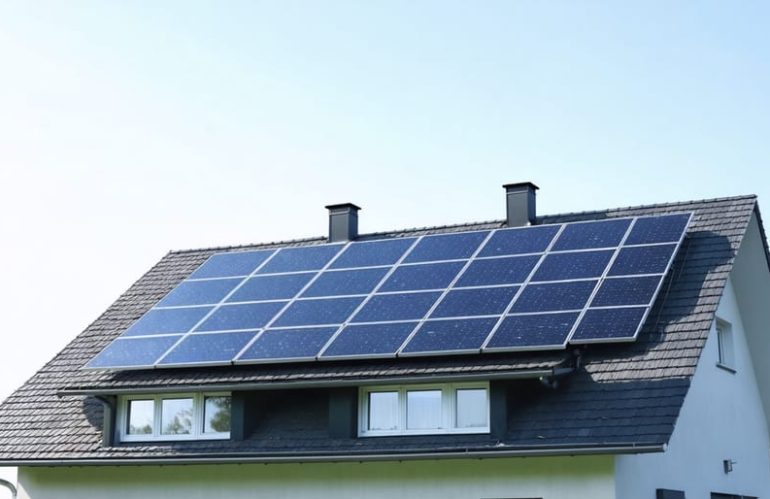
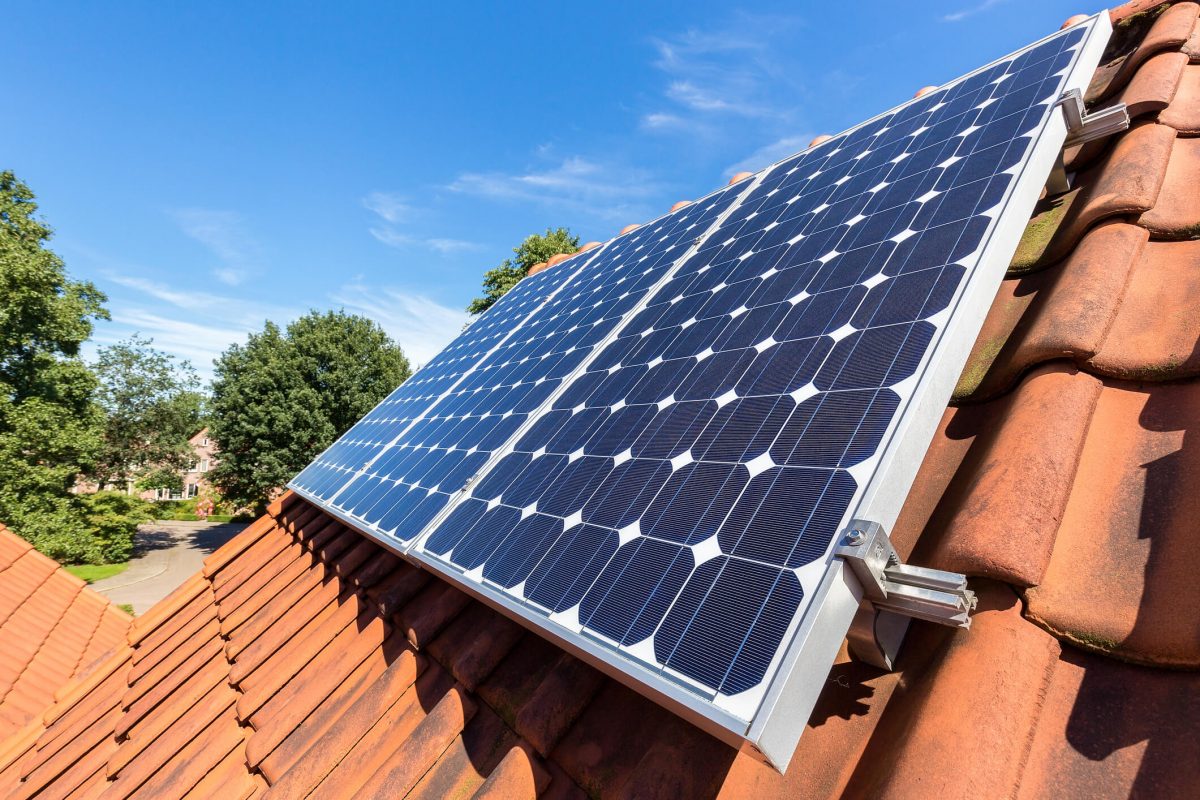
Residential solar panels have transformed from a niche eco-friendly choice to a mainstream energy solution, with dimensions playing a crucial role in their effectiveness and installation success. Today’s standard residential solar panels typically measure between 65 to 71 inches long and 39 to 41 inches wide, dimensions carefully engineered to balance power generation with practical rooftop installation requirements. These measurements aren’t just numbers – they represent the sweet spot between maximum sun exposure and structural feasibility for most American homes.
Understanding solar panel dimensions is essential for homeowners planning their energy future. Whether you’re considering a new installation or upgrading an existing system, panel size directly impacts everything from energy production capacity to installation costs. Modern panels optimize space utilization while delivering impressive power outputs of 350-400 watts per panel, making them significantly more efficient than earlier generations.
The relationship between panel dimensions and roof space has become increasingly important as more homeowners embrace solar energy. With the average residential installation requiring 20-24 panels to meet household energy needs, proper dimensioning ensures maximum power generation without compromising your home’s structural integrity or aesthetic appeal. This practical knowledge empowers homeowners to make informed decisions about their solar investment while ensuring optimal system performance for decades to come.
Standard Residential Solar Panel Dimensions
Common Panel Sizes and Specifications
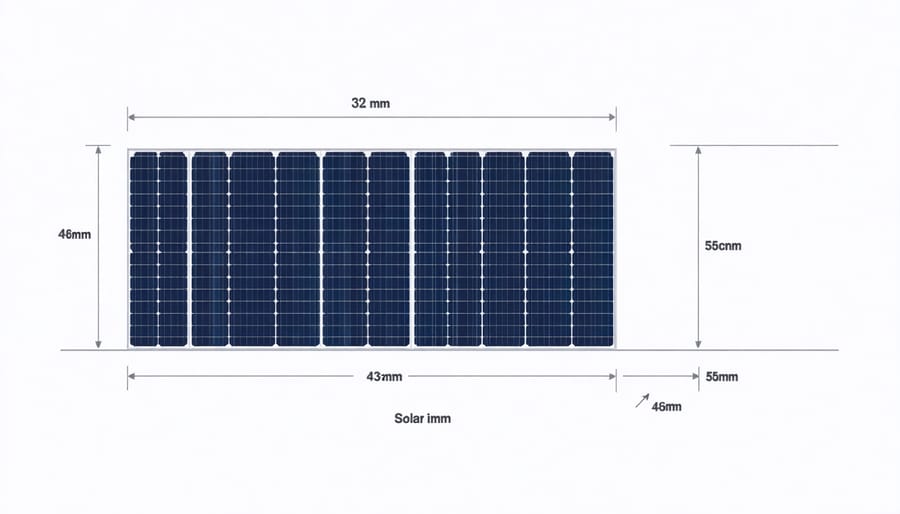
Among the various solar panel types available today, residential panels typically come in standardized dimensions to ensure compatibility and easy installation. The most common size for residential solar panels is approximately 65 inches by 39 inches (165 cm x 99 cm), with a depth of 1.5 to 2 inches. These standard dimensions allow panels to generate between 250 and 400 watts of power under optimal conditions.
For homeowners with space constraints, compact panels measuring 61.3 inches by 41.2 inches are also available. These slightly smaller units still deliver efficient power output while requiring less roof space. Most manufacturers maintain these consistent dimensions across their product lines to simplify installation and maximize roof coverage.
The weight of typical residential panels ranges from 33 to 50 pounds (15-23 kg), making them manageable for professional installation while ensuring structural stability. This standardization helps homeowners easily plan their solar installations and calculate how many panels will fit on their available roof space.
Space Requirements and Roof Coverage
When planning your solar installation, understanding how panel dimensions affect roof coverage is crucial for maximizing energy production. A typical residential solar panel takes up about 17.5 square feet, and most homes need between 15 and 20 panels for optimal energy production. This means you’ll need approximately 260 to 350 square feet of usable roof space for a standard installation.
Your roof’s available space and orientation play key roles in panel layout. South-facing roof sections typically offer the best sun exposure in North America, though east and west-facing installations can still be effective. Keep in mind that you’ll need some empty roof space around the panels for maintenance access and proper ventilation – typically about 2-3 feet from roof edges and peaks.
The dimensions of modern solar panels allow for flexible arrangement patterns, helping installers work around obstacles like chimneys, vents, and skylights. Most installation companies can create custom layouts that maximize your roof’s available space while maintaining aesthetic appeal and optimal energy production. Remember to factor in local setback requirements, which may restrict how close panels can be placed to roof edges.
How Dimensions Affect System Performance
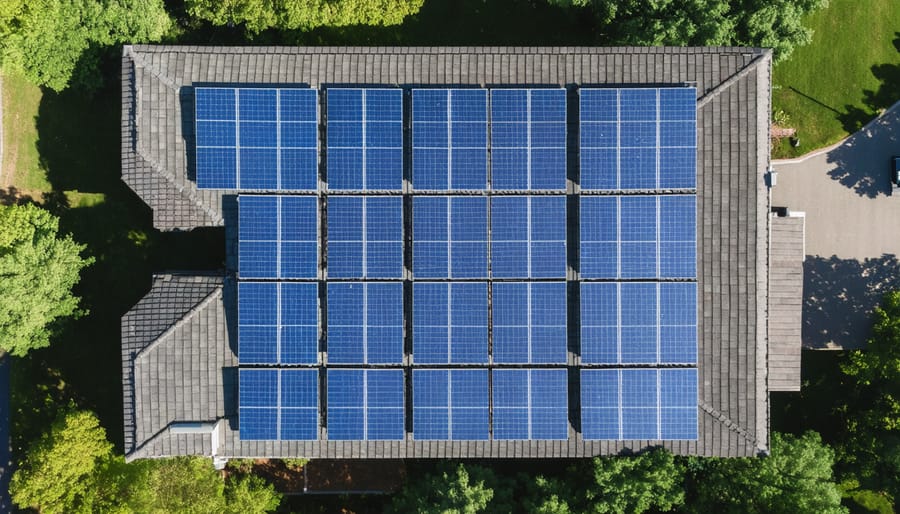

Power Output vs. Panel Size
When it comes to solar panels, size directly influences their energy-generating potential. The relationship between panel dimensions and power output performance follows a straightforward principle: larger panels generally produce more electricity, though efficiency also plays a crucial role.
Most residential solar panels range from 65 to 72 inches long and 39 to 41 inches wide, offering power outputs between 250 and 400 watts per panel. For example, a standard 65″ x 39″ panel typically generates around 250-300 watts, while a larger 72″ x 41″ panel can produce up to 400 watts under optimal conditions.
However, bigger isn’t always better for every home. Your available roof space, budget, and energy needs should guide your panel selection. A smaller, high-efficiency panel might generate more power than a larger, less efficient one. Modern panels are becoming increasingly efficient, allowing homeowners to generate more power from smaller surface areas.
Consider this practical example: A 300-watt panel measuring 65″ x 39″ requires about 17.6 square feet of roof space. To generate 6kW of power (a typical household system), you’d need twenty such panels, occupying approximately 352 square feet. Alternatively, using 400-watt panels could reduce the required space by 25%, while achieving the same total output.
When planning your solar installation, focus on finding the sweet spot between panel size, efficiency, and your available space. This balance ensures you maximize your energy generation without compromising your roof’s aesthetic or structural integrity.
Monitoring Considerations
The size and layout of your solar panels play a crucial role in how effectively you can monitor and maintain your solar energy system. Larger panels typically offer more surface area for smart monitoring sensors, making it easier to track performance and detect issues early. Most modern residential panels come equipped with built-in monitoring capabilities that work regardless of panel dimensions, but the spacing between panels can affect how easily you can access and clean them.
When panels are installed with appropriate gaps (typically 1-2 inches between rows), maintenance becomes much more manageable. These spaces allow for proper airflow, which helps prevent debris accumulation and makes it easier to spot potential problems like hot spots or microcracks. The height and arrangement of your panels also influence how readily you can inspect them – panels mounted closer to the roof’s edge are generally easier to examine than those placed higher up.
For optimal monitoring, consider how your panel dimensions affect shade patterns throughout the day. Larger panels might be more susceptible to partial shading, which monitoring systems need to track carefully. Most modern monitoring solutions can provide detailed performance data for individual panels, helping you identify if certain panel sizes or positions are contributing to reduced efficiency.
Regular maintenance is simpler when panels are arranged in easily accessible configurations. Standard residential panel dimensions (about 65 inches by 39 inches) typically allow for comfortable spacing between rows, making it possible to clean panels and check connections without awkward reaching or specialized equipment. Remember that proper spacing also helps prevent snow and leaves from accumulating between panels, reducing the frequency of required maintenance visits.
Optimal Panel Sizing for Your Home
Roof Configuration Assessment
Before installing solar panels, it’s essential to assess your roof’s available space and configuration to determine the optimal panel layout. Start by measuring your roof’s total square footage, paying special attention to unobstructed areas that receive direct sunlight throughout the day. A south-facing roof section is ideal, though east and west-facing surfaces can also work effectively.
Consider your roof’s pitch angle, as this affects both solar efficiency and installation requirements. The optimal angle typically matches your geographical latitude, though most residential roofs between 30-45 degrees work well for solar installations. Also, note any obstacles such as chimneys, vents, or skylights that might create shadows or require spacing adjustments.
A good rule of thumb is to leave about 2-3 feet of space from roof edges and peaks for safety and maintenance access. Additionally, maintain proper spacing between panels for ventilation and service accessibility. Most residential installations require about 20-24 panels for optimal energy production, so plan accordingly.
Remember to factor in local building codes and HOA regulations, which might dictate setback requirements or placement restrictions. It’s also wise to consider future roof maintenance needs when planning your panel layout. Working with a professional solar installer can help ensure your roof configuration maximizes both energy production and system longevity while meeting all local requirements.
Energy Needs and Panel Dimensions
Choosing the right solar panel dimensions starts with understanding your household’s energy needs. The average American home uses about 900 kWh per month, but your actual usage may vary significantly based on your lifestyle and appliances. To determine the ideal panel size for your home, first review your electricity bills from the past year to calculate your average monthly consumption.
A typical residential solar panel produces between 250-400 watts of power, depending on its size and efficiency. For example, a standard 60-cell panel measuring 65 x 39 inches can generate around 300 watts under ideal conditions. To meet the energy needs of an average household, you might need 20-24 of these panels, requiring approximately 400-500 square feet of roof space.
However, larger 72-cell panels, measuring roughly 78 x 39 inches, can produce more power per panel (350-400 watts), potentially reducing the total number of panels needed. This could be beneficial if you have limited roof space but high energy demands.
Remember that panel dimensions aren’t just about power output – they must also work with your available roof space and local building codes. Consider factors like roof orientation, shade patterns, and structural support when planning your solar array. Many homeowners find that mixing different panel sizes helps optimize their system’s performance while working within spatial constraints.
Installation and Monitoring Best Practices
Installation Considerations
When installing solar panels, proper placement and mounting considerations are crucial for optimal performance. Your roof should have enough unshaded space to accommodate the panels’ dimensions while maintaining appropriate spacing for ventilation and maintenance access. Most installations require about 3-4 inches of space between panels and 6-12 inches from roof edges.
Roof pitch also plays a vital role in panel placement. The ideal angle typically matches your geographical latitude, though most residential roofs already provide acceptable angles between 30-45 degrees. Consider that each panel requires secure mounting points, usually four per panel, with proper spacing to ensure structural integrity.
Weight distribution is another key factor. A typical 60-cell residential panel weighs about 40 pounds, so your roof must be able to support the combined weight of all panels plus mounting hardware. For multiple rows of panels, allow sufficient space between rows to prevent shading and ensure easy access for maintenance.
Remember to account for setback requirements from your local building codes, which often mandate specific clearances around roof edges and peaks. These requirements ensure firefighter access and comply with safety regulations. Always consult with a qualified solar installer who can assess your specific roof dimensions and recommend the most efficient panel layout.
Performance Tracking
Monitoring your solar panel system’s performance is crucial for ensuring optimal energy production and long-term savings. Modern solar installations come with sophisticated system health monitoring tools that help you track performance based on your specific panel configuration.
Most monitoring systems provide real-time data through user-friendly mobile apps or web portals. These tools display key metrics like daily energy production, panel efficiency, and potential issues that might affect performance. For typical residential installations with 60-cell panels, you can expect to monitor individual panel output, helping you quickly identify if any panels are underperforming.
The layout and positioning of your panels directly impact how you’ll track their performance. South-facing panels typically generate the most power, and your monitoring system should reflect this in its readings. Pay attention to seasonal variations in output – panels generally produce more energy during summer months when days are longer and the sun is higher in the sky.
For optimal tracking, ensure your monitoring system accounts for your specific panel arrangement. String configurations, panel tilt angles, and any potential shade patterns should all be properly configured in your monitoring setup. This allows for accurate performance benchmarking and helps you spot any deviations from expected production levels quickly.
Regular monitoring helps maintain system efficiency and ensures you’re maximizing your investment in solar energy. Many systems can even send automated alerts when performance drops below expected levels, making it easier to maintain your system’s health proactively.
Understanding residential solar panel dimensions is crucial for a successful solar installation and optimal system performance. Most residential panels measure between 65 and 71 inches long, 39 to 41 inches wide, and around 1.5 to 2 inches thick, making them suitable for most home rooftops. These standard dimensions allow for efficient energy production while maintaining aesthetic appeal.
When planning your solar installation, remember that panel dimensions affect not only the physical layout but also your system’s overall performance. Larger panels typically generate more power, but they must be balanced against available roof space and structural considerations. Modern monitoring systems can track the performance of individual panels, helping you ensure each unit operates at peak efficiency regardless of its size.
The good news is that today’s solar panels are more efficient than ever, meaning you can generate substantial power even with limited roof space. Regular monitoring of your system through user-friendly apps and interfaces allows you to track energy production and identify any maintenance needs quickly. This combination of appropriate sizing and active monitoring ensures your solar investment continues to deliver maximum benefits.
As you move forward with your solar project, work with qualified installers who can help you select the right panel dimensions for your specific needs while ensuring proper monitoring capabilities are in place. This approach will help you maximize both energy production and long-term system reliability.









