Zoning regulations and environmental science intersect powerfully when planning residential solar installations, directly impacting both property values and the environmental benefits of solar installation. Local zoning codes determine optimal panel placement, setback requirements, and height restrictions while protecting crucial environmental factors like soil stability, water drainage, and wildlife corridors. Understanding these regulations before installation saves homeowners thousands in potential compliance issues while maximizing energy production potential. Modern zoning laws increasingly favor renewable energy adoption, offering streamlined permits and reduced restrictions for properties meeting sustainable development criteria. This shift reflects growing recognition that thoughtful land use planning enhances both environmental protection and clean energy deployment, creating win-win scenarios for homeowners and communities alike.
Understanding Solar Panel Land Use Requirements
Space Requirements for Residential Solar
When planning a residential solar installation, understanding space requirements is crucial for system sizing. A typical 5kW solar system, which meets the average American home’s energy needs, requires approximately 300-400 square feet of roof or ground space. This accounts for about 20 solar panels, each measuring roughly 65 by 39 inches.
For smaller homes or partial solar solutions, a 3kW system needs about 180-240 square feet, while larger 10kW systems require 600-800 square feet. These measurements assume standard efficiency panels in optimal conditions. South-facing installations typically need less space due to maximum sun exposure.
Keep in mind that your available space should include additional room for maintenance access and safety setbacks from roof edges. Ground-mounted systems need extra clearance to prevent shading and allow for landscaping maintenance. The exact space requirements can vary based on panel efficiency, roof angle, and local climate conditions.
Before installation, consider future needs – leaving some additional space for system expansion can be a smart long-term strategy. Most homeowners find that their existing roof space easily accommodates their solar needs while maintaining curb appeal.
Optimal Property Positioning
The ideal placement of your property’s features can significantly impact both energy efficiency and environmental benefits. South-facing orientations typically offer optimal sun exposure for solar panels, while strategic tree placement on the east and west sides provides natural cooling during summer months. Consider positioning buildings to maximize natural light and ventilation, reducing the need for artificial lighting and cooling systems.
When planning your landscape, group plants with similar water needs together to create efficient irrigation zones. Position rain gardens and bioswales in natural low points to manage stormwater runoff effectively. For maximum energy savings, locate deciduous trees on the south side of buildings to provide shade in summer while allowing warming sunlight during winter months.
Driveways and parking areas should be situated to minimize impervious surfaces and positioned away from natural drainage patterns. Consider using permeable materials in these areas to reduce runoff. Garden spaces benefit from being placed where they’ll receive adequate sunlight while being protected from strong winds. Remember that proper positioning not only enhances environmental performance but can also increase property value and reduce long-term maintenance costs.

Local Zoning Laws and Solar Rights
Understanding Solar Access Rights
Solar access rights are fundamental protections that ensure homeowners can harness solar energy without interference from neighboring structures or vegetation. These rights typically guarantee your ability to install solar panels and maintain access to sunlight, which is essential for optimal energy production.
Most states have specific laws protecting your solar access rights. These regulations often prevent homeowners’ associations (HOAs) from outright banning solar installations, though they may still impose reasonable aesthetic requirements. Some jurisdictions even offer solar easements, which are voluntary agreements between property owners to ensure continued access to sunlight.
Understanding your local solar rights is crucial before installation. Key considerations include:
– Height restrictions on neighboring buildings
– Tree growth and maintenance requirements
– Setback requirements from property lines
– Historic district regulations
– HOA guidelines and restrictions
To protect your solar access rights, consider these steps:
1. Review local zoning codes and ordinances
2. Document existing sun exposure patterns
3. Discuss plans with neighbors
4. Obtain necessary permits before installation
5. Consider establishing a solar easement
Many municipalities now recognize the importance of protecting solar access and have implemented “solar-ready” zoning codes. These forward-thinking regulations ensure new developments don’t inadvertently block solar potential for existing or future installations, helping preserve your investment and supporting sustainable energy adoption.
Common Zoning Restrictions
Common residential zoning restrictions typically focus on preserving neighborhood character while ensuring environmental protection. Height limitations often restrict structures to 35 feet or less, which can affect solar panel placement on rooftops. Setback requirements mandate minimum distances between buildings and property lines, potentially limiting ground-mounted solar installations.
Many areas have specific lot coverage restrictions, typically allowing 30-40% of the lot to be covered by structures. This affects where you can place ground-mounted solar arrays while maintaining compliance. Some neighborhoods also have historic preservation ordinances that may require special permits for visible solar installations.
Navigating these restrictions starts with researching your local zoning codes. Most municipalities provide online access to zoning regulations, making it easier to understand what’s permitted on your property. Working with a qualified solar installer who knows local regulations can help identify the best installation options within zoning constraints.
If you encounter challenges, consider these solutions:
– Request a variance for special circumstances
– Explore alternative mounting locations
– Use low-profile solar panels
– Consider community solar options if on-site installation isn’t feasible
Remember that many communities are updating their zoning codes to be more solar-friendly, recognizing the environmental and economic benefits of renewable energy. Some areas even offer expedited permits for solar installations that meet specific criteria.
Environmental Impact Assessment
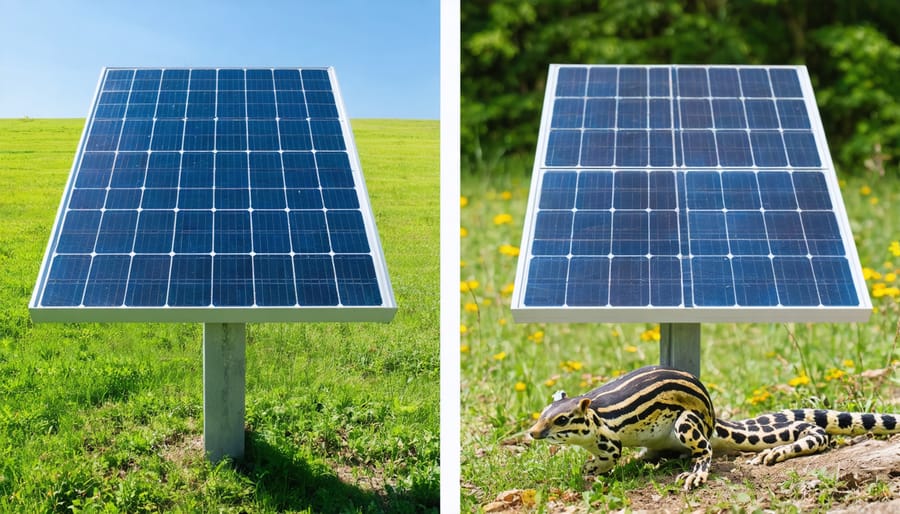

Habitat Preservation
When installing solar panels, maintaining the delicate balance of your local ecosystem is crucial. Understanding key ecosystem preservation considerations helps ensure your solar project benefits both your energy needs and the surrounding environment.
Start by conducting a site assessment to identify important natural features like mature trees, native plant species, and wildlife corridors. Where possible, position panels to minimize disruption to existing vegetation. Consider installing elevated mounting systems that allow natural groundcover to thrive underneath, creating beneficial microhabitats for local wildlife.
For ground-mounted installations, incorporate native plant species around the array to support pollinators and local biodiversity. These plants can also help prevent soil erosion and reduce maintenance needs. Create wildlife passages between panel rows and maintain buffer zones around sensitive habitat areas.
Timing your installation during seasons when local wildlife is less active can minimize disturbance. Work with your installer to develop a construction plan that protects existing root systems and soil structure. Many homeowners find that thoughtful solar installation actually enhances their property’s ecological value while generating clean energy, creating a win-win situation for both environmental sustainability and energy independence.
Sustainable Land Management
When installing solar panels, implementing sustainable land management practices is crucial for maintaining ecological balance while maximizing energy production. Start by conducting a thorough site assessment to identify optimal panel placement that minimizes impact on existing vegetation and wildlife habitats. Consider using elevated mounting systems that allow for dual land use, such as grazing or growing shade-tolerant plants underneath the panels.
Proper drainage planning helps prevent soil erosion and maintains ground stability. Install permeable ground covers or native vegetation between panel rows to reduce water runoff and support local biodiversity. This approach also helps control dust, which can reduce panel efficiency.
For larger installations, create wildlife corridors and maintain buffer zones around sensitive areas. Use environmentally friendly cleaning methods and avoid harsh chemicals when maintaining panels. Regular monitoring of soil health and local ecosystem impacts helps ensure long-term sustainability.
Consider implementing pollinator-friendly landscaping beneath and around solar arrays, which can enhance local biodiversity while supporting agricultural needs. This approach not only benefits the environment but can also improve community acceptance of solar installations and potentially increase property values.
Maximizing Property Value with Smart Solar Planning
Strategic solar panel placement can significantly boost your property’s market value while maximizing energy production. Studies show that homes with well-planned solar installations sell for 4.1% more on average compared to similar properties without solar. The key lies in thoughtful placement that considers both aesthetics and efficiency.
To optimize your property’s value, start by evaluating your roof’s orientation and angle. South-facing installations typically generate the most energy in North America, making them particularly attractive to potential buyers. Consider positioning panels where they’re visible enough to showcase your home’s sustainability features but not so prominent that they dominate the architectural aesthetic.
Work with local zoning officials to understand setback requirements and height restrictions that could affect panel placement. Many municipalities now offer expedited permits for solar installations that meet specific aesthetic guidelines, potentially increasing your home’s appeal to future buyers.
Smart solar planning also involves landscaping considerations. Strategic tree placement can help reduce energy costs while maintaining curb appeal. Consider the growth patterns of nearby trees and their potential impact on solar production over time.
Remember that proper documentation of your solar system’s performance, maintenance records, and warranty information can further enhance your property’s value. Buyers appreciate well-maintained systems with proven energy savings, making your investment even more valuable in the long run.
Making your property solar-ready doesn’t have to be complicated. By understanding local zoning requirements, conducting proper environmental assessments, and working with qualified professionals, you can successfully navigate the path to sustainable energy. Remember that solar installations not only benefit the environment but can also increase your property value and significantly reduce your energy costs. Take the first step today by checking your local zoning codes and consulting with solar professionals in your area. With careful planning and consideration of environmental factors, you can join the growing community of homeowners contributing to a cleaner, more sustainable future while enjoying the advantages of renewable energy for years to come.









