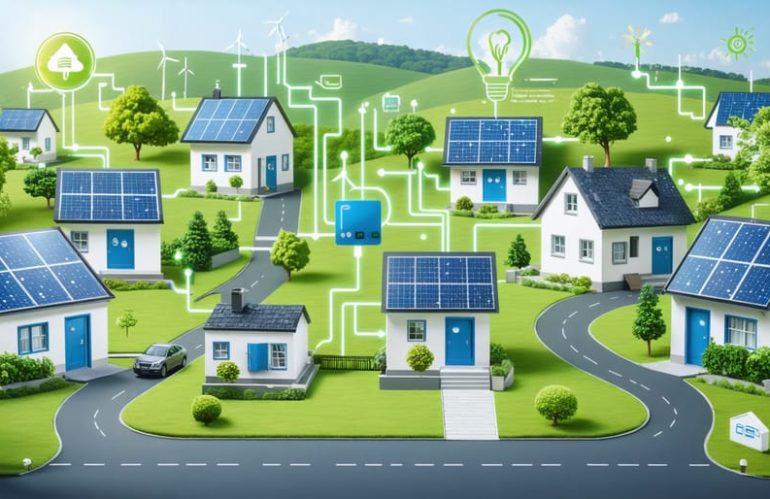
Transform your home’s energy future by joining a decentralized storage network – a revolutionary approach to maximizing solar power investment through community-based energy sharing. Instead of relying solely on individual batteries, homeowners now connect their solar storage systems into a neighborhood-wide network, creating a resilient power grid that reduces costs and enhances energy independence. This innovative solution allows excess solar energy to flow where it’s needed most, cutting electricity bills by up to 30% while providing backup power during outages. By participating in a decentralized storage network, you’re not just optimizing your own energy usage – you’re helping build a more sustainable, reliable energy ecosystem for your entire community.
What Is a Decentralized Solar Storage Network?
The Building Blocks
A decentralized storage network relies on three essential components working together seamlessly. First, battery systems form the backbone, storing excess solar energy for later use. Modern lithium-ion batteries offer excellent performance and longevity, while emerging technologies like flow batteries show promise for larger-scale storage.
Smart meters are the network’s eyes and ears, continuously monitoring energy flow between homes, batteries, and the grid. These intelligent devices track production, consumption, and sharing in real-time, ensuring fair distribution and accurate accounting of energy exchanges.
The control system acts as the network’s brain, using sophisticated software to manage energy flow efficiently. It automatically determines when to store excess energy, when to share it with neighbors, and when to draw from the grid. This smart technology optimizes energy use based on factors like weather forecasts, peak usage times, and electricity rates, maximizing both environmental and financial benefits for all participants.
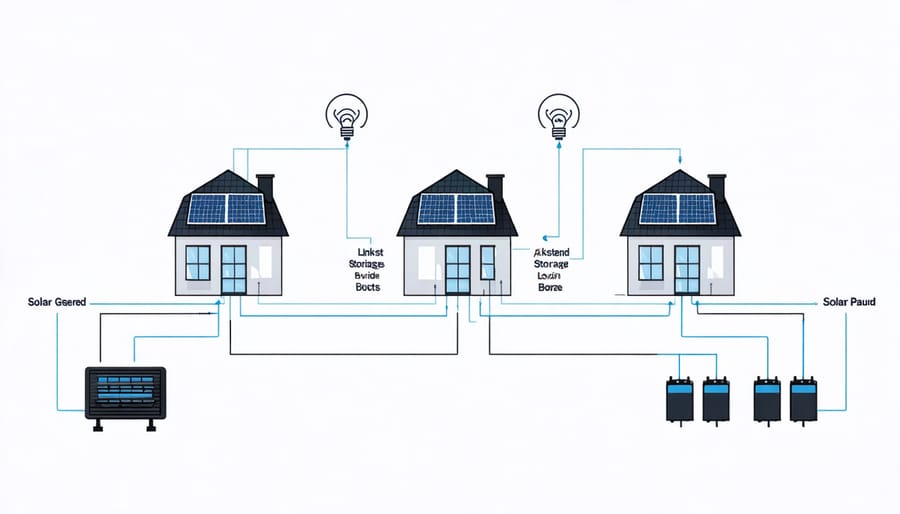
How Power Sharing Works
In a decentralized storage network, connected homes share power through a sophisticated yet straightforward system. When your solar panels generate excess electricity, instead of sending it back to the grid, it’s stored in a network of batteries shared among participating households. Think of it like a neighborhood power pool – when one home has extra energy, others can draw from it as needed.
The system automatically manages this distribution using smart technology that monitors each home’s energy production and consumption in real-time. During peak sunlight hours, homes producing more power than they need contribute to the shared storage. Later, when the sun sets or during high-demand periods, homes can access this stored energy, reducing their reliance on the grid.
This sharing mechanism ensures that solar power is used efficiently within the community, maximizing the benefits of renewable energy while minimizing waste and grid dependency.

Benefits for Homeowners
Lower Energy Costs
When homeowners join a decentralized storage network, they can significantly reduce their energy costs through smart resource sharing and efficient demand management. By pooling energy storage capacity with neighbors, participants can tap into stored energy during peak hours when electricity rates are highest, avoiding premium pricing from utility companies.
The network automatically optimizes energy distribution, drawing from shared batteries when grid prices surge and storing excess solar power when rates are low. This intelligent load balancing can reduce individual electricity bills by 20-30% on average, with some households reporting even greater savings during high-demand seasons.
Beyond daily cost reductions, members benefit from decreased equipment expenses since the shared network eliminates the need for each home to maintain a full-sized battery system. The collaborative approach also extends battery life through balanced usage patterns, reducing long-term replacement costs.
Additionally, many utility companies offer special incentives and rebates for households participating in decentralized storage networks, recognizing their contribution to grid stability and peak demand reduction. These financial benefits make the initial investment in shared storage systems even more attractive for budget-conscious homeowners.

Enhanced Grid Reliability
Decentralized storage networks significantly enhance grid reliability by creating a robust, interconnected power backup system across multiple properties. When traditional power lines fail, these networks activate seamlessly, allowing communities to share stored energy resources and maintain power supply. Unlike standalone battery backup systems, networked storage provides extended protection against outages by pooling energy resources.
This collaborative approach ensures that even during extended blackouts, essential services remain operational. Homes connected to the network can maintain power for refrigeration, heating, cooling, and critical medical equipment. The system automatically balances load distribution, preventing any single storage unit from being depleted too quickly.
During normal operations, the network also helps stabilize voltage fluctuations and manage peak demand periods, resulting in more consistent power quality for all connected homes. This enhanced reliability not only provides peace of mind but also protects sensitive electronic equipment from damage caused by sudden power disruptions.
Environmental Impact
Decentralized storage networks significantly reduce the environmental impact of traditional data centers by distributing energy consumption across multiple locations. Unlike centralized systems that require massive cooling infrastructure and constant power supply, these networks optimize energy use through smart load balancing and efficient resource sharing.
The community-based approach of decentralized storage naturally promotes sustainability. When neighbors share storage capacity, it reduces the need for individual battery installations, minimizing manufacturing waste and resource consumption. This collaborative model also encourages the use of renewable energy sources, as excess solar power can be stored and distributed effectively throughout the network.
Studies show that decentralized storage networks can reduce carbon emissions by up to 30% compared to traditional storage solutions. The system’s ability to manage peak demand periods more efficiently also lessens the strain on the power grid, contributing to a more sustainable energy ecosystem for everyone.
Getting Started with Shared Storage
Equipment Requirements
To participate in a decentralized storage network, you’ll need several key components. The foundation is a solar battery system, typically a lithium-ion or similar advanced storage solution, with sufficient capacity for your household needs. Quality inverters are essential for converting stored energy between AC and DC power, ensuring seamless integration with both your home and the grid.
A reliable internet connection is crucial, as it enables your system to communicate with the network and respond to energy demands in real time. Smart battery monitoring systems are also necessary to optimize performance and track energy flow.
You’ll need a smart meter compatible with bi-directional energy flow, allowing you to both contribute to and draw from the network. A home energy management system helps coordinate these components efficiently. Most systems also require a gateway device that serves as the communication hub between your equipment and the network.
All equipment should meet local safety standards and be installed by certified professionals to ensure proper integration with existing infrastructure.
Finding Network Partners
Finding like-minded neighbors and local solar enthusiasts is easier than ever in today’s connected world. Start by checking social media platforms, particularly Facebook and Nextdoor, for local renewable energy groups. Many communities already have established solar circles where members share experiences and resources.
Local environmental organizations and sustainability meetups are excellent places to connect with potential storage network partners. These groups often host informational sessions and workshops where you can meet others interested in shared solar solutions.
Consider reaching out to your local solar installers, as they typically maintain networks of customers and can facilitate introductions. Many also organize community events or maintain referral programs that can help you connect with nearby solar homeowners.
Online platforms dedicated to renewable energy communities, such as Solar United Neighbors or local energy cooperatives, provide structured ways to join or create storage networks. These organizations often offer guidance on forming partnerships and navigating the technical and legal aspects of shared storage systems.
Don’t forget to check with your utility company, as some offer community solar programs or can connect you with existing storage networks in your area.
Future of Neighborhood Power Sharing
The future of neighborhood power sharing is looking increasingly bright, with innovative technologies and community-focused solutions reshaping how we think about energy storage. Smart microgrids are emerging as game-changers, allowing neighbors to efficiently share stored solar energy based on real-time needs and availability. These systems use artificial intelligence to predict usage patterns and automatically distribute power where it’s needed most.
Virtual power plants (VPPs) are gaining traction, connecting multiple home battery systems into a unified network that can respond to grid demands more effectively than individual systems. This collaborative approach not only maximizes storage efficiency but also creates new opportunities for homeowners to earn money by participating in energy markets.
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing how neighbors trade excess energy, enabling secure, automated transactions without intermediaries. This peer-to-peer trading system ensures fair compensation while maintaining transparency and trust within the community.
Mobile apps are making it easier than ever for homeowners to monitor and manage their energy sharing. These user-friendly interfaces allow residents to track their contribution to the community grid, view their savings, and adjust their participation levels with just a few taps.
Looking ahead, experts predict the integration of electric vehicles into neighborhood storage networks, using parked cars as additional battery capacity during peak hours. This vehicle-to-grid technology could significantly expand community storage capabilities without requiring additional infrastructure investment.
As these technologies mature, we’re seeing more neighborhoods adopt “energy sovereignty” models, where communities become largely self-sufficient in their power needs while maintaining grid connection as a backup. This trend towards local energy independence is reshaping how we think about power distribution and community cooperation.
Decentralized storage networks represent a revolutionary step forward in how we store and share energy within our communities. By participating in these networks, homeowners can significantly reduce their energy costs while contributing to a more sustainable future. The combination of solar panels, battery storage, and smart grid technology creates a resilient system that benefits everyone involved.
As we’ve explored, these networks offer numerous advantages: increased energy independence, reduced utility bills, improved grid stability, and a smaller carbon footprint. The technology is becoming more accessible and affordable each year, making it an increasingly attractive option for environmentally conscious homeowners.
If you’re considering joining or creating a decentralized storage network in your community, start by reaching out to local solar installers and energy cooperatives. They can provide specific information about available programs and incentives in your area. By taking action today, you’ll be part of an innovative solution that’s reshaping our energy landscape for the better. The future of energy is collaborative, sustainable, and community-driven – and it starts with you.









