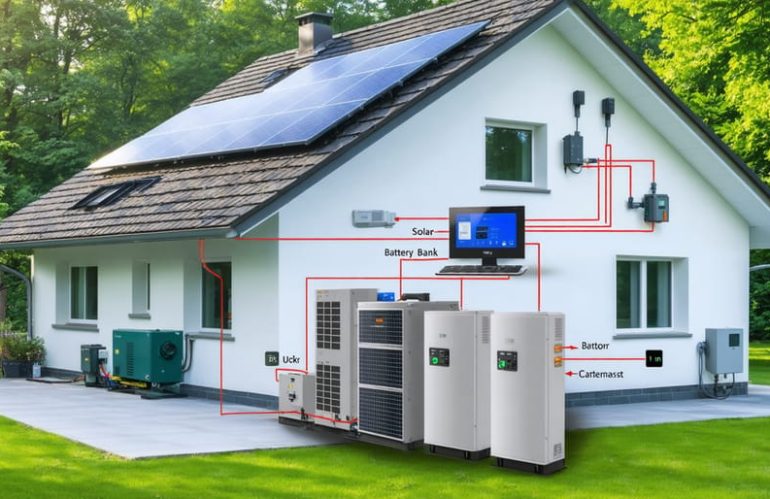
Harness the power of modern energy independence with a grid-tied solar system featuring solar battery backup systems. This intelligent hybrid solution combines the reliability of utility power with the self-sufficiency of solar energy storage, ensuring your home stays powered during outages while reducing monthly electricity costs. Unlike traditional grid-only systems, a battery-backed setup provides the best of both worlds: clean solar power for daily use, seamless backup during blackouts, and the ability to sell excess energy back to the grid. Understanding the components and connections in these systems empowers homeowners to make informed decisions about their energy future, whether upgrading an existing solar installation or planning a new one. Today’s advanced system diagrams reveal how solar panels, charge controllers, batteries, and inverters work together to create a resilient home energy ecosystem that pays for itself over time.
Understanding Grid-Tied Solar Systems with Battery Backup
Essential Components
A grid-tied solar system with battery backup consists of several key components working together seamlessly. Solar panels, typically mounted on your roof, capture sunlight and convert it into DC electricity. These panels connect to a charge controller, which regulates the power flow to protect your batteries from overcharging.
The battery bank stores excess energy for later use, especially during power outages or nighttime. Modern lithium-ion batteries offer better efficiency and longer life compared to traditional lead-acid options. A hybrid inverter serves as the system’s brain, converting DC power from your panels and batteries into AC power for home use while managing power flow between your home, the grid, and your battery storage.
The automatic transfer switch is crucial for safety, disconnecting your home from the grid during outages while allowing your solar system to power essential appliances. A smart meter tracks energy production and consumption, helping you monitor system performance.
Additional components include mounting hardware, wiring, and safety disconnects. Many systems also feature monitoring systems that let you track performance through smartphone apps, giving you complete control over your home’s energy management.
How Power Flows Through Your System
In a grid-tied solar system with battery backup, power flows through multiple pathways to maximize efficiency and ensure continuous electricity supply. During daylight hours, your solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, which first passes through the inverter to convert it from DC to AC power. This electricity then follows one of three routes: directly powering your home’s immediate needs, charging your battery bank for later use, or feeding excess energy back into the utility grid.
When your solar panels produce more power than needed, the extra electricity can either charge your batteries or flow to the grid, earning you credits through net metering. During nighttime or cloudy days, your home draws power first from the battery backup system. If the batteries run low, the system automatically switches to grid power, ensuring uninterrupted service.
In case of a grid outage, the system disconnects from the utility grid and operates independently. Your critical loads continue receiving power from your solar panels during the day and battery backup at night, providing energy security when you need it most.
Benefits of Battery Backup Systems
Reliable Power During Outages
A grid-tied solar system with battery backup provides crucial power security during grid outages, ensuring your home stays functional when you need it most. Unlike standard grid-tied systems that shut down during blackouts, these hybrid systems seamlessly switch to battery power, maintaining 24/7 power reliability for your essential home systems.
During an outage, your battery backup automatically activates within milliseconds, powering critical loads like refrigeration, medical equipment, home security systems, and basic lighting. Modern battery systems are smart enough to prioritize your most important appliances, extending backup duration by efficiently managing power distribution.
The system continues to generate solar power during daylight hours, charging your batteries while simultaneously powering your home. This creates a sustainable cycle that can maintain power for extended periods, especially when combined with conscious energy usage. Many homeowners find peace of mind knowing their food won’t spoil, security systems remain active, and their families can maintain comfortable living conditions despite external power disruptions.
For areas prone to severe weather or unreliable grid service, this reliable backup solution proves invaluable. The system’s automatic switching means no manual intervention is required, ensuring uninterrupted power even when you’re away from home.
Energy Bill Savings
A grid-tied solar system with battery backup offers substantial financial benefits through smart energy management. By storing excess solar power during peak production hours, you can effectively reduce your energy bills by utilizing your stored energy during high-rate periods.
During sunny days, your system generates free electricity from solar panels, powering your home and charging the batteries simultaneously. When electricity rates are highest – typically during evening peak hours – you can draw power from your batteries instead of the grid, avoiding premium pricing. This strategic energy use can lead to savings of 40-70% on monthly utility bills.
The battery backup system also protects you from rising utility rates. As electricity costs continue to climb nationwide, your stored solar energy becomes increasingly valuable. Many utility companies offer net metering programs, allowing you to earn credits for excess power you send to the grid, further maximizing your savings.
Additionally, some regions offer time-of-use rate plans, where electricity costs vary throughout the day. With battery storage, you can optimize your energy consumption by using stored power during expensive rate periods and grid power during cheaper ones, maximizing your financial benefits while maintaining energy independence.
System Operation Modes
Normal Grid Operation
During normal grid operation, your solar panels generate clean electricity that powers your home’s needs first. Any excess energy flows through the inverter and into the utility grid, earning you credits through net metering. At the same time, your battery system maintains a partial charge, ready to provide backup power if needed.
When your solar panels produce more electricity than you’re using, the surplus energy takes two paths. The primary route sends power back to the grid, while a portion charges your backup batteries. This ensures you’re maximizing both your energy savings and emergency preparedness.
At night or during cloudy days when your panels produce less power, your home draws electricity from the grid as needed. The system automatically manages this transition, so you’ll never notice any interruption in power. Your battery backup remains charged and on standby, monitoring grid conditions continuously.
The smart inverter acts as the system’s brain, coordinating power flow between your panels, home, batteries, and the grid. It ensures your batteries maintain optimal charge levels while maximizing the financial benefits of your solar generation. This seamless operation means you can enjoy reliable, clean energy while reducing your carbon footprint and electricity bills.
Throughout normal operation, the system requires no intervention from you, working quietly to provide sustainable power for your home.
Backup Power Mode
During a power outage, your grid-tied solar system with battery backup seamlessly switches to backup power mode, ensuring your essential appliances and devices stay running. This automatic transition happens in a fraction of a second, so you might not even notice the grid power has gone down.
In backup mode, your solar panels continue generating electricity, which flows directly to your backup loads through the inverter while simultaneously charging your batteries. The system prioritizes powering your critical loads first, such as refrigerators, medical equipment, and basic lighting, while storing excess energy in the batteries for nighttime use.
Your battery bank serves as your personal power reservoir, providing electricity when the sun isn’t shining. The smart inverter manages power flow efficiently, balancing between immediate power needs and battery charging to maximize your energy independence during outages.
It’s important to note that backup power mode typically doesn’t support your entire home’s power usage. Instead, it focuses on your pre-selected critical loads circuit, which helps extend battery life during extended outages. Most homeowners choose to backup essential circuits that keep their homes comfortable and functional until grid power returns.
When utility power is restored, the system automatically switches back to grid-tied operation, seamlessly returning to normal function without any intervention needed from you.
Making the Right Choice for Your Home
When planning your grid-tied solar system with battery backup, proper sizing and selection are crucial for optimal performance and cost-effectiveness. Start by analyzing your household’s average daily energy consumption through recent utility bills. This baseline helps determine the solar array size needed to meet your power requirements.
Consider your backup power goals – do you want to run your entire home during outages, or just essential appliances? The answer will significantly impact choosing the right battery system for your needs. Most homeowners opt to back up critical loads like refrigeration, lighting, and medical equipment rather than whole-house backup, which can substantially reduce system costs.
Your roof’s available space and orientation also play vital roles in system sizing. South-facing roof sections typically offer optimal solar exposure, though east and west-facing arrays can still be effective. Consider any shade from trees or nearby structures that might impact panel performance throughout the day.
Climate factors into both solar panel and battery sizing. Areas with frequent cloudy weather may need larger arrays to generate sufficient power. Similarly, regions prone to extended power outages might benefit from additional battery capacity to ensure longer backup duration.
Don’t forget to factor in future needs. If you’re planning to add an electric vehicle or expecting increased energy usage, design your system with some room for expansion. While oversizing can increase initial costs, it’s often more economical than adding capacity later.
Work with a qualified solar installer to conduct a detailed site assessment and energy audit. They can help balance your power needs, backup requirements, and budget constraints while ensuring compliance with local building codes and utility requirements. Remember that the most expensive system isn’t always the best choice – the ideal solution is one that meets your specific needs efficiently and reliably.
A grid-tied solar system with battery backup represents a smart investment in your home’s energy future. By combining the reliability of grid power with the independence of solar energy storage, you’re creating a resilient and sustainable power solution for your household. The system’s ability to seamlessly switch between power sources ensures you’ll never be left in the dark during outages while continuing to benefit from lower electricity bills and reduced carbon emissions.
As we’ve explored throughout this guide, these hybrid systems offer the best of both worlds: clean energy generation, emergency backup power, and the security of grid connection. While the initial setup may seem complex, working with qualified installers and understanding the basic components makes the process straightforward and manageable.
Remember that investing in a grid-tied solar system with battery backup not only increases your home’s value but also provides immediate and long-term financial benefits through reduced energy costs and potential tax incentives. Additionally, you’ll be contributing to a cleaner environment while gaining energy independence.
Ready to take the next step? Consider reaching out to certified solar installers in your area for a personalized assessment of your home’s solar potential. With proper planning and implementation, you’ll be well on your way to a more sustainable and secure energy future for your home.