Solar panels have become the cornerstone of residential clean energy, with standard sizes designed to balance power output and installation practicality. Most residential solar panels measure between 65 to 75 inches long and 39 to 41 inches wide, delivering power outputs ranging from 250 to 400 watts per panel. Understanding these dimensions is crucial for homeowners planning their solar installation, as panel size directly impacts system efficiency, roof coverage, and overall energy production potential.
Today’s residential solar market offers remarkable flexibility in panel configurations, making it possible to optimize installations for virtually any home. Whether you’re working with limited roof space or aiming to maximize power generation, modern solar panel dimensions accommodate diverse installation needs while maintaining the aesthetic appeal of your property. This standardization has revolutionized home solar adoption, making it easier than ever for homeowners to transition to clean, renewable energy while ensuring their investment fits perfectly with their home’s architecture.
Understanding Standard Solar Panel Dimensions
Residential Panel Size Specifications
Today’s residential solar panels come in remarkably consistent sizes, making it easier for homeowners to plan their solar installations. A typical residential solar panel measures about 65 inches by 39 inches (roughly 5.4 feet by 3.25 feet), though slight variations exist between manufacturers. These standard dimensions provide approximately 15 square feet of surface area per panel.
Weight is another crucial consideration for rooftop installations. Most residential panels weigh between 40 to 50 pounds, which is well within the structural capacity of most properly maintained roofs. This means a typical 10-panel system would add about 400-500 pounds to your roof’s load, distributed across a large area.
When planning your solar installation, remember to account for mounting hardware and spacing requirements. Installers typically recommend leaving 2-3 inches of space between panels for proper airflow and maintenance access. For a typical 6kW system (around 20 panels), you’ll need approximately 350-400 square feet of usable roof space.
Different manufacturers may offer slightly different dimensions, but they generally stay within these ranges to maintain compatibility with standard mounting systems and installation practices. Some companies also produce compact panels for spaces with unique requirements, though these typically deliver less power output compared to standard-sized panels.
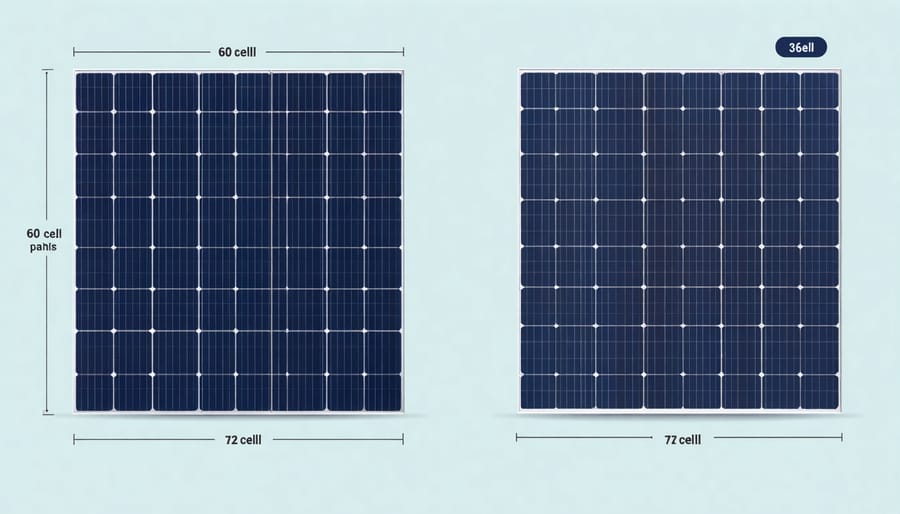
60-Cell vs. 72-Cell Panels
When choosing residential solar panels, you’ll typically encounter two main configurations: 60-cell and 72-cell panels. 60-cell panels are the most popular choice for homes, measuring about 5.4 feet by 3.25 feet. These panels offer an excellent balance of power output and manageable size, making them perfect for most residential roofs.
72-cell panels are slightly larger, measuring approximately 6.5 feet by 3.25 feet. While they generate more power per panel, their bigger size can make installation trickier on some residential roofs. These panels were traditionally used for commercial installations, but they’re becoming increasingly popular in residential settings where roof space allows.
The choice between the two often comes down to your specific needs. 60-cell panels are ideal if you have limited roof space or complex roof angles. They’re also lighter and easier to handle during installation. 72-cell panels might be your better option if you have plenty of roof space and want to maximize power generation with fewer panels overall. Both types offer similar efficiency ratings and durability, so your decision should focus on your roof configuration and energy needs.
Customization Options for Your Roof
Panel Arrangement Patterns
Standard residential solar panels can be arranged in various patterns to maximize your roof’s available space and solar potential. Following a proper solar panel layout blueprint ensures optimal energy production while maintaining visual appeal.
The most common arrangement is the landscape pattern, where panels are installed horizontally in rows. This configuration works well for most pitched roofs and allows for efficient use of space. Portrait orientation, with panels mounted vertically, is another option that can be particularly useful for narrow roof sections or areas with specific shading patterns.
For maximum coverage, installers often use a grid pattern, arranging panels in neat rows and columns. This approach typically delivers the highest power output per square foot. Some installations may require split arrays, where panels are installed in separate groups to work around roof obstacles like vents or chimneys.
Staggered patterns can be employed when working with complex roof shapes or to avoid shaded areas. This flexible approach ensures you can still achieve good solar coverage even with architectural challenges.
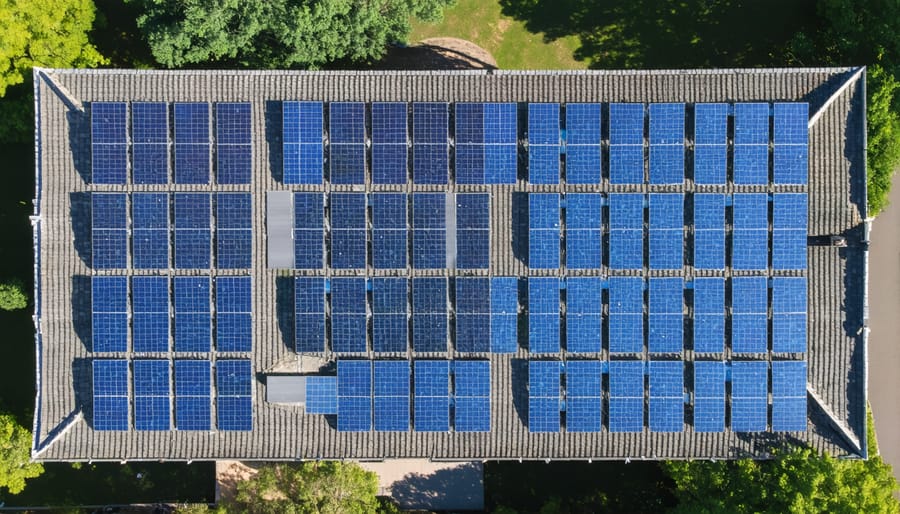

Space-Saving Solutions
Limited roof space doesn’t mean you have to give up on your solar dreams. Modern solar solutions offer several smart alternatives for homes with space constraints. High-efficiency panels can generate more power in a smaller area, allowing you to maximize energy production with fewer panels. Some manufacturers now offer compact panels specifically designed for tight spaces, delivering similar output to standard sizes while taking up less room.
Another effective approach is using half-cut cell panels, which maintain high performance even in partially shaded conditions and can be arranged more flexibly on your roof. For homes with unusual roof configurations, custom-sized panels are available, though they may come at a premium. You might also consider bifacial panels, which capture sunlight from both sides, potentially increasing energy production without requiring additional space.
Some homeowners opt for alternative mounting solutions, such as ground-mounted systems in their yard or creative installations on pergolas and carports. These options can supplement roof panels or serve as standalone solutions when roof space is at a premium. Working with an experienced solar installer can help you identify the most efficient space-saving solution for your specific situation.
Choosing the Right Panel Size
Energy Needs Assessment
Before selecting solar panels, it’s crucial to understand your household’s energy consumption. Start by reviewing your past 12 months of electricity bills to determine your average monthly usage in kilowatt-hours (kWh). This baseline helps you calculate how many panels you’ll need for optimal energy production.
A typical American home uses around 900 kWh per month, but your needs may vary based on factors like house size, appliance efficiency, and climate. To estimate your panel requirements, divide your monthly energy usage by the average solar panel output in your area. For example, if you use 900 kWh monthly and each panel produces 30 kWh per month, you’d need approximately 30 panels.
Consider future changes in your energy consumption, such as buying an electric vehicle or adding new appliances. It’s often wise to include a buffer in your calculations to accommodate increased energy needs. Many homeowners opt for systems that can cover 100-120% of their current usage to ensure long-term sufficiency and maximize their investment in solar energy.
Remember that local weather patterns, roof orientation, and shading will affect your panels’ efficiency, so consult with a solar professional for the most accurate assessment of your needs.
Understanding standard residential solar panel sizes is crucial for making an informed decision about your home’s solar installation. While typical panels measure around 65 by 39 inches, remember that your solar solution can be customized to suit your specific needs. Consider factors like your roof space, energy requirements, and local climate when planning your installation. The next step is to get a professional assessment of your property to determine the optimal panel configuration. By working with qualified installers and taking advantage of available incentives, you can create an efficient solar system that maximizes both energy production and cost savings. Ready to start your solar journey? Contact local solar providers for detailed quotes and personalized recommendations based on your home’s unique characteristics.









