Harness the untapped potential of wind energy to power your home while slashing electricity bills and reducing your carbon footprint. As residential wind turbines become more efficient and affordable, homeowners across America are discovering how this renewable energy source can transform their energy independence. Today’s compact wind energy systems can generate anywhere from 2 to 10 kilowatts of power – enough to meet 50-90% of a typical household’s electricity needs.
The revolution in home wind power isn’t just about environmental benefits. Modern turbines integrate seamlessly with existing power systems, operate quietly, and can pay for themselves within 5-10 years through energy savings and government incentives. Whether you live in a rural area with abundant wind resources or a suburban neighborhood with moderate breeze patterns, new turbine designs can help you capture this infinite energy source.
From small rooftop installations to pole-mounted systems, residential wind power options have evolved to suit various property sizes and energy needs. Understanding your local wind patterns, zoning laws, and energy requirements is the first step toward joining the growing community of homeowners generating clean, renewable energy right where they live.
How Home Wind Energy Systems Actually Work
Key Components of a Home Wind System
A home wind energy system consists of three essential components working together to power your home. The wind turbine, typically mounted on a tall pole or tower, captures wind energy through its rotating blades. Modern residential turbines are designed to be quiet and efficient, with most models ranging from 2 to 10 kilowatts in capacity, depending on your home’s energy needs.
The second crucial component is the inverter, which converts the turbine’s DC power into AC power that your home can use. Quality inverters ensure smooth power delivery and can automatically switch between wind power and grid power when needed.
The connection system ties everything together, including:
– The charge controller, which prevents battery overcharging
– Batteries for energy storage (optional but recommended)
– Safety disconnect switches
– Power meter to monitor energy production
– Grid-tie equipment for connecting to your local power grid
Many systems also include monitoring equipment that lets you track performance through smartphone apps or web interfaces. This helps you optimize your system’s efficiency and ensure it’s operating at peak performance throughout the year.
Grid Connection vs. Battery Storage
When setting up a residential wind energy system, homeowners typically choose between grid connection and battery storage – or a combination of both. Grid-connected systems allow you to feed excess power back to the utility grid, potentially earning credits through net metering programs. This setup works well in areas with reliable grid access and favorable net metering policies.
Battery storage systems, while initially more expensive, offer independence from the grid and ensure power availability during outages. Modern batteries can integrate seamlessly with smart home automation systems to optimize energy usage based on your consumption patterns.
Many homeowners opt for hybrid systems, combining grid connection with a smaller battery backup. This arrangement provides the best of both worlds: the ability to earn credits from excess production while maintaining power security during outages. The choice ultimately depends on your energy goals, local utility policies, and budget considerations. Your local renewable energy installer can help determine the most cost-effective solution for your specific situation.
Is Your Home Right for Wind Energy?
Location and Wind Speed Requirements
The success of a home wind energy system largely depends on your location and local wind conditions. The ideal spot for a residential wind turbine requires average wind speeds of at least 10-12 miles per hour. Most areas in the United States have detailed wind resource maps that can help you determine if your location is suitable.
Your property should have enough open space, as turbines need to be placed away from obstacles like tall buildings, trees, and other structures that could block wind flow or create turbulence. Generally, the turbine should be at least 30 feet higher than anything within 300 feet of its location.
Rural and suburban areas typically offer better conditions for wind energy systems than urban settings. Coastal regions, hilltops, and open plains are particularly favorable locations due to their consistent wind patterns. However, even if you live in an area with moderate wind speeds, modern small-scale turbines are becoming increasingly efficient at harvesting energy from lower wind speeds.
Before installation, it’s essential to check local zoning laws and homeowners’ association regulations, as some areas have height restrictions or specific requirements for wind turbines. Many communities also require permits and may have noise ordinances that affect turbine placement. Consider working with a local wind energy professional who can assess your specific location and recommend the most suitable turbine size and placement for your property.
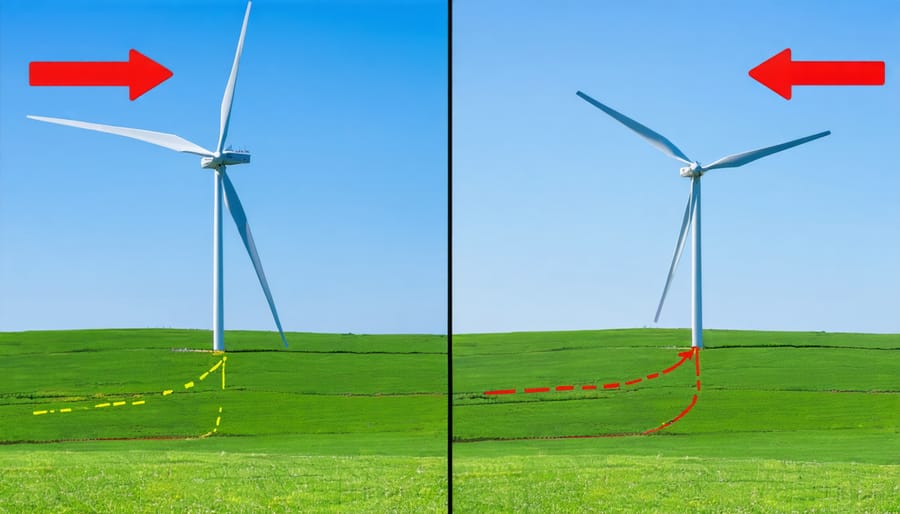

Property Size and Zoning Rules
Before installing a residential wind turbine, it’s essential to understand your property’s requirements and local zoning regulations. Most residential wind systems need at least one acre of land, with larger properties offering better potential for optimal wind exposure. The ideal location should be free from obstacles like tall buildings, trees, or hills that could block or disturb wind flow.
Typical height requirements for residential wind turbines range from 80 to 120 feet, which allows them to access stronger, more consistent winds above ground-level turbulence. However, local zoning laws often restrict structure heights, so it’s crucial to check your area’s regulations before proceeding.
Many municipalities have specific ordinances governing wind turbine installations, including setback requirements (distance from property lines), noise limitations, and visual impact considerations. Some areas may require special permits or variances, while others might have homeowners’ association restrictions that affect installation.
To ensure compliance, consult your local planning department early in the process. They can provide information about:
– Height restrictions
– Setback requirements
– Noise regulations
– Permit requirements
– Environmental impact assessments
– Safety considerations
Remember that zoning laws vary significantly between jurisdictions, and some areas may be more wind-energy friendly than others. Working with a qualified installer who understands local regulations can help navigate these requirements successfully.
Real Cost Benefits of Home Wind Power
Initial Investment vs. Long-term Savings
Installing a residential wind turbine system typically requires an initial investment of $15,000 to $35,000, depending on your home’s energy needs and location. While this upfront cost may seem substantial, it’s important to consider the long-term financial benefits that make wind energy an attractive investment for many homeowners.
The average payback period for a residential wind system ranges from 6 to 12 years, depending on factors such as local wind conditions, electricity rates, and available incentives. Many states offer tax credits, rebates, and grants that can significantly reduce your initial costs. Additionally, the federal investment tax credit (ITC) allows you to deduct 30% of the installation cost from your federal taxes.
Once installed, wind turbines can reduce or eliminate your monthly electricity bills, potentially saving $1,500 to $3,000 annually. Modern turbines are designed to last 20-25 years, providing decades of clean energy production. When paired with energy monitoring solutions, you can optimize your system’s performance and maximize your savings.
Maintenance costs are relatively low, typically averaging $300-500 per year for routine inspections and occasional repairs. Many manufacturers offer warranties covering major components for 5-10 years, providing additional peace of mind for your investment. As electricity rates continue to rise, the value proposition of wind energy becomes even more compelling, making it an increasingly attractive option for forward-thinking homeowners.
Available Tax Incentives and Rebates
Installing a residential wind energy system can be more affordable than you might think, thanks to various financial incentives and rebates. The Federal Residential Renewable Energy Tax Credit allows you to claim up to 30% of your installation costs through 2032. Many states offer additional tax credits, grants, or rebates that can be combined with federal incentives.
Property tax exemptions are available in several states, meaning your home’s increased value from wind installation won’t raise your property taxes. Some utility companies provide performance-based incentives, paying you for the renewable energy your system generates. Net metering programs also allow you to sell excess electricity back to the grid, further reducing your energy costs.
Local municipalities may offer specialized grants or low-interest loans for renewable energy projects. Rural homeowners can access USDA REAP grants, covering up to 25% of project costs. Remember to check with your local energy office, as available incentives vary by location and can change annually. Consulting with a renewable energy tax professional can help ensure you maximize available benefits.
Combining Wind and Solar: The Perfect Match
Benefits of a Hybrid System
Combining wind and solar power creates a powerful duo that maximizes your home’s renewable energy potential. While wind turbines excel during stormy weather and nighttime hours, solar panels capture energy during sunny days, creating a complementary system that ensures more consistent power generation throughout the year.
This hybrid approach significantly reduces your reliance on the grid, as one system typically compensates when the other’s production is low. During winter months, when solar panels receive less sunlight, wind turbines often perform better due to stronger winds. Conversely, summer’s longer days boost solar production when winds are typically calmer.
A hybrid system also makes better use of your energy storage solutions. With two power sources, your batteries maintain more consistent charge levels, extending their lifespan and improving overall system efficiency. Additionally, having dual power sources often means you can install smaller individual systems while achieving better energy coverage, potentially reducing initial installation costs.
Many homeowners find that hybrid systems qualify for multiple renewable energy incentives, potentially increasing their tax benefits and rebates compared to single-source installations.
Smart Integration Strategies
For optimal performance, combining wind energy with other renewable sources creates a more reliable and efficient home energy system. The key is implementing automated energy management systems that can seamlessly switch between power sources based on availability and demand.
Start by installing a hybrid inverter that can handle both wind and solar inputs. This allows your home to capture energy during both sunny and windy conditions, maximizing your renewable energy production throughout the day. Consider adding battery storage to store excess energy for use during low-production periods.
Smart meters and monitoring systems help track your energy production and consumption patterns, allowing you to optimize your usage. Schedule high-energy activities like laundry or dishwashing during peak production times to maximize your renewable energy usage.
For homes in areas with seasonal variations, consider a wind-solar combination that takes advantage of winter winds and summer sunshine. This complementary approach ensures more consistent energy production throughout the year, reducing your reliance on grid power and lowering your overall energy costs.
Maintenance and Care Tips
Regular Maintenance Schedule
Regular maintenance ensures your residential wind turbine system operates efficiently and safely. Schedule these essential checks throughout the year:
Monthly:
• Visual inspection of blades for damage
• Check tower and support structure
• Monitor system performance through smart power monitoring
• Clear debris around the base
Quarterly:
• Tighten all bolts and fasteners
• Lubricate moving parts
• Check electrical connections
• Test emergency brake system
Annually:
• Professional inspection of all components
• Blade cleaning and balancing
• Gearbox oil change
• Battery system assessment
• Full electrical system review
Additionally, schedule professional maintenance visits every 2-3 years for comprehensive system overhauls. After extreme weather events, conduct immediate inspections to ensure system integrity. Keep detailed maintenance records and set calendar reminders for upcoming service dates. This proactive approach extends your system’s lifespan and maintains optimal performance.
Common Issues and Solutions
While home wind energy systems are generally reliable, you may encounter some common issues. Intermittent power generation during low-wind periods can be addressed by installing a hybrid system with solar panels or maintaining a grid connection as backup. Unusual noises often indicate loose components or the need for lubrication – schedule regular maintenance checks to prevent these issues. Bird collisions can be minimized by installing visual deterrents or choosing turbine designs with protective features.
If your system’s performance drops, check for debris on the blades, damaged components, or improper alignment. Most issues can be resolved through routine maintenance or simple adjustments. For electrical problems, always consult a certified technician. Some homeowners report interference with TV or radio signals, which can typically be solved by repositioning antennas or using signal boosters.
Remember to keep maintenance records and follow manufacturer guidelines to prevent common problems before they occur. Most issues are preventable with proper installation and regular upkeep.
Wind energy offers homeowners a powerful way to reduce their environmental impact while potentially saving significantly on energy costs. By understanding the key aspects of residential wind power – from turbine selection and installation requirements to maintenance needs and financial incentives – you can make an informed decision about whether wind energy is right for your home.
If you’re considering wind power, start by assessing your property’s wind resources and local zoning regulations. A professional wind energy consultant can help evaluate your site’s potential and recommend appropriate system sizes. Remember that successful wind power implementation depends on factors like average wind speeds, property size, and local building codes.
The next steps include obtaining necessary permits, selecting a qualified installer, and exploring financing options. Many states offer tax incentives, grants, and rebate programs that can significantly reduce your initial investment. Additionally, consider connecting with local renewable energy organizations or homeowners who have already installed wind systems to learn from their experiences.
While residential wind power requires careful planning and upfront investment, the long-term benefits often outweigh the initial challenges. With proper maintenance, a wind system can provide clean, renewable energy for 20-30 years, offering both environmental and financial returns. Whether you’re ready to install a complete wind power system or just beginning your research, taking action toward renewable energy is a step toward a more sustainable future.