Design your home to reduce energy consumption by up to 50% through strategic architectural planning. Orient windows southward to maximize natural light and solar heat gain during winter months, while incorporating deep eaves to block intense summer sun. Position living spaces on the south side of the home to capitalize on passive solar benefits, with utility areas serving as thermal buffers on the north side.
Modern energy-efficient home designs blend time-tested passive strategies with cutting-edge technology, delivering substantial utility savings while enhancing comfort. Strategic window placement, advanced insulation systems, and smart home integration create a sustainable living space that maintains consistent temperatures year-round. These thoughtful design choices not only slash energy bills but also increase property value, offering both immediate and long-term financial benefits.
Today’s energy-efficient homes prove that environmental responsibility and luxury aren’t mutually exclusive. By incorporating these design principles from the ground up, homeowners can create spaces that are both comfortable and conscious of their environmental impact, while enjoying significantly lower operating costs throughout the home’s lifetime.
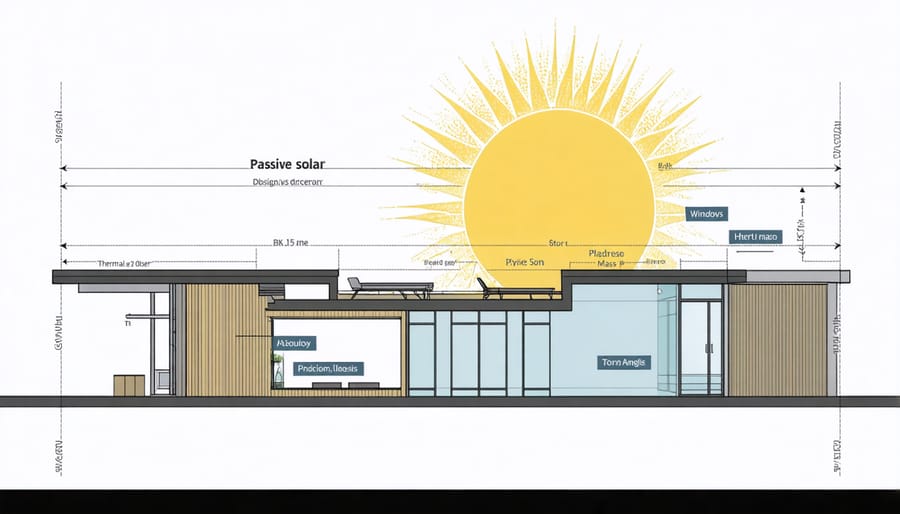
Passive Solar Design Principles
Strategic Window Placement
Strategic window placement is a cornerstone of energy-efficient home design, helping you harness natural light and heat while reducing energy costs. South-facing windows are your greatest allies, capturing maximum sunlight during winter months when the sun sits lower in the sky. Plan for these windows to occupy about 7-12% of your home’s total floor area for optimal solar gain.
East and west-facing windows require careful consideration, as they can lead to unwanted heat gain in summer. Use smaller windows on these sides and incorporate adjustable shading devices like exterior awnings or deciduous trees to manage seasonal sun exposure.
North-facing windows (in the Northern Hemisphere) provide consistent, indirect light without significant heat gain. These are perfect for spaces where you want natural light without glare, such as home offices or art studios.
For maximum efficiency, position larger windows higher on walls to allow light to penetrate deeper into your living spaces. Consider clerestory windows or skylights in central areas to reduce the need for artificial lighting during daylight hours. Remember to choose double or triple-pane windows with appropriate Low-E coatings to maintain indoor temperature control while maximizing natural light benefits.
Thermal Mass Solutions
Thermal mass solutions play a vital role in maintaining comfortable temperatures while reducing energy costs. These solutions work by absorbing and storing heat during warm periods and releasing it when temperatures drop. Materials like concrete, brick, and stone are excellent choices for thermal mass, acting as natural temperature regulators throughout your home.
Strategic placement of thermal mass elements is crucial for maximum effectiveness. Concrete floors or stone walls exposed to direct sunlight can capture heat during winter days and gradually release it during cooler evenings. In summer, these same materials can help keep your home cooler by absorbing excess heat.
Water features and containers can also serve as effective thermal mass elements, as water has exceptional heat-retention properties. Consider incorporating a decorative indoor water wall or strategically placed water containers in sunlit areas.
Modern phase-change materials (PCMs) offer an innovative approach to thermal mass. These materials can be incorporated into walls and ceilings, changing their physical state to store and release heat at specific temperatures. This technology provides efficient temperature regulation without the bulk of traditional thermal mass materials.
For optimal results, combine thermal mass solutions with proper insulation and ventilation. This creates a comprehensive system that maintains comfortable temperatures year-round while minimizing energy consumption.
Insulation and Air Sealing Strategies
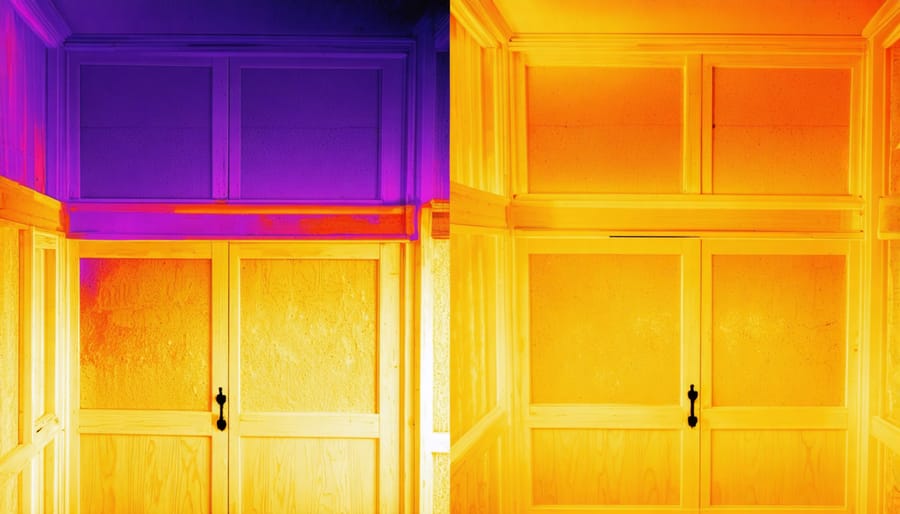

Advanced Insulation Materials
Modern insulation materials have revolutionized home energy efficiency, offering homeowners powerful ways to maintain comfortable temperatures while reducing energy costs. Spray foam insulation leads the pack with its superior air-sealing capabilities and high R-value per inch. Available in both open-cell and closed-cell varieties, spray foam can reduce heating and cooling costs by up to 50% when properly installed.
Mineral wool (also known as rockwool) has gained popularity for its fire resistance, sound dampening properties, and excellent thermal performance. Made from recycled materials, it’s an environmentally conscious choice that’s also naturally moisture-resistant.
Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs) represent a cutting-edge solution, combining insulation and structural elements into a single component. These panels offer exceptional thermal performance and can speed up construction time significantly.
For eco-conscious homeowners, natural insulation options like cellulose (made from recycled paper) and sheep’s wool provide effective alternatives. These materials offer good thermal performance while having minimal environmental impact.
Vacuum Insulated Panels (VIPs), though currently more expensive, represent the future of insulation technology. With R-values up to five times higher than traditional materials, they’re ideal for projects where space is at a premium.
When selecting insulation, consider factors beyond R-value, such as air-sealing properties, moisture resistance, and environmental impact. The right combination of materials can create a highly efficient thermal envelope that pays dividends in comfort and energy savings.
Air Leakage Prevention
Air leakage can account for up to 40% of your home’s heating and cooling losses, making it crucial to identify and seal common escape points. Start by conducting a simple visual inspection of your home’s envelope, paying special attention to areas where different building materials meet. Common leak points include windows and door frames, electrical outlets, pipe penetrations, and attic hatches.
For a more thorough assessment, perform the DIY smoke test: Hold a lit incense stick near potential leak areas on a windy day and watch how the smoke moves. Horizontal smoke movement indicates an air leak that needs addressing. Professional energy auditors can provide even more detailed assessments using blower door tests and infrared cameras.
Once you’ve identified leaks, seal them using appropriate materials. Use weatherstripping for movable components like doors and windows, and apply caulk for static gaps around window frames and baseboards. For larger gaps, expanding foam sealant works best, particularly around pipe penetrations and in rim joists.
Don’t forget often-overlooked areas like electrical boxes, which can be sealed with foam gaskets, and chimney flues, which require fire-rated materials. Even small fixes like installing outlet gaskets behind switch plates can make a noticeable difference in preventing drafts.
Remember to maintain proper ventilation while sealing your home. Focus on unintentional air leaks while ensuring controlled ventilation through proper systems.
Smart HVAC Integration
Zoned Climate Control
Zoned climate control represents a smart approach to managing your home’s temperature efficiently. By dividing your home into distinct climate zones, you can heat or cool specific areas based on occupancy and usage patterns, potentially reducing your energy consumption by 20-30%.
Modern zoning systems use a combination of programmable thermostats and automated dampers in your ductwork to direct conditioned air where it’s needed most. For example, you can maintain a comfortable temperature in your living areas during the day while reducing heating or cooling in unused bedrooms, or adjust temperatures for different floors to account for natural heat rise.
The benefits extend beyond energy savings. Zoned systems eliminate hot and cold spots throughout your home, improve overall comfort, and reduce wear on your HVAC equipment. They’re particularly effective in homes with multiple stories, large windows, or rooms that receive different amounts of sunlight throughout the day.
Setting up a zoned system is straightforward with today’s smart home technology. Many systems can be controlled via smartphone apps, allowing you to adjust temperatures remotely and create custom schedules that match your family’s routine.
Heat Recovery Systems
Heat recovery ventilation systems (HRV) are game-changers in maintaining indoor air quality while minimizing energy waste. These smart systems work by capturing heat from stale outgoing air and using it to warm fresh incoming air, recovering up to 85% of heat that would otherwise be lost. During summer, the process reverses, helping to pre-cool incoming air.
Modern HRV systems come with advanced features like humidity control and automatic adjustment based on indoor air quality. For homeowners, this means consistently fresh air without the energy penalty of traditional ventilation. The initial investment typically pays for itself within 2-5 years through reduced heating and cooling costs.
Beyond energy savings, these systems offer significant health benefits by filtering incoming air and maintaining optimal humidity levels. They’re particularly valuable in well-insulated homes where air tightness is essential for energy efficiency but can lead to poor ventilation if not properly managed.
Installation is most cost-effective during new construction but can also be retrofitted into existing homes. For maximum efficiency, pair your HRV system with proper insulation and air sealing measures.
Solar-Ready Design Elements
Roof Orientation and Structure
The roof of your home plays a crucial role in maximizing energy efficiency, particularly when incorporating renewable energy solutions like solar panels. For optimal solar energy collection, aim for a roof pitch between 30-45 degrees, with the primary surface facing south in the Northern Hemisphere. This orientation captures maximum sunlight throughout the year, potentially reducing your energy bills by up to 30%.
Consider designing your roof with adequate structural support for solar panel installation, even if you’re not planning to install them immediately. This forward-thinking approach saves money on future modifications. Include sufficient roof space without obstructions like chimneys or vents on the south-facing portion.
Modern roof designs can incorporate both aesthetics and functionality. Light-colored roofing materials reflect heat, reducing cooling costs in summer. Additionally, proper roof overhangs provide shade during hot months while allowing beneficial solar gain during winter.
For homes in snowy regions, steeper pitches help prevent snow accumulation, ensuring consistent solar panel performance. Remember to plan for easy maintenance access and include proper waterproofing measures to protect your investment over time.
Electrical System Planning
Proper electrical system planning is crucial for creating an energy-efficient home that’s ready for future technological upgrades. Start by designing a comprehensive electrical blueprint that includes dedicated circuits for high-efficiency appliances and smart home systems. Consider installing a smart electrical panel that allows for detailed energy monitoring and remote control of various circuits.
Pre-wiring for solar power integration is essential, even if you’re not planning to install panels immediately. This includes running conduit from your roof to your electrical panel area, installing a proper grounding system, and leaving adequate space for future inverter installation. Plan for battery storage capabilities by designating a cool, dry area near your main electrical panel.
Include multiple electrical zones throughout your home to enable selective power management. Strategic placement of outlets and lighting circuits can reduce phantom energy loss and optimize natural light usage. Consider installing automated lighting controls and smart switches that can be programmed for optimal energy usage.
Don’t forget to plan for electric vehicle charging capabilities by installing appropriate wiring and circuit capacity in your garage. This forward-thinking approach ensures your home remains adaptable to emerging technologies while maintaining peak energy efficiency.

Smart Technology Integration
Modern homes are becoming increasingly intelligent, with smart home automation systems playing a crucial role in optimizing energy usage. These innovative technologies transform how we manage our home’s energy consumption, making efficiency both convenient and effortless.
Smart thermostats lead the way in energy management, learning your schedule and preferences while automatically adjusting temperature settings for optimal comfort and savings. These devices can reduce heating and cooling costs by up to 15% through intelligent scheduling and remote control capabilities.
Automated lighting systems with motion sensors ensure lights are only on when needed, while smart LED bulbs allow for scheduled dimming and remote control through smartphone apps. Smart plugs and power strips can automatically cut power to devices in standby mode, eliminating phantom energy drain that typically accounts for 10% of home electricity use.
Energy monitoring systems provide real-time feedback on power consumption, helping homeowners identify energy-hungry appliances and adjust their usage patterns accordingly. Many systems even send alerts when unusual energy spikes occur, preventing waste and unexpected bills.
Smart window treatments can automatically adjust based on sunlight and temperature, helping to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures while reducing HVAC load. When integrated with weather forecasts, these systems can proactively prepare your home for incoming weather changes.
The beauty of modern smart technology lies in its seamless integration. Through a single smartphone app or voice command, homeowners can control multiple systems simultaneously, creating automated routines that maximize energy efficiency without sacrificing comfort. These investments typically pay for themselves through reduced energy bills while adding convenience and value to your home.
Creating an energy-efficient home is more than just a trend – it’s a smart investment in your future and our planet’s wellbeing. By incorporating the design principles we’ve explored, from passive solar orientation to advanced insulation techniques, you can significantly reduce your energy consumption while creating a more comfortable living space.
Remember that energy efficiency doesn’t have to mean compromising on style or comfort. Modern technologies and innovative design approaches make it possible to achieve both sustainability and aesthetic appeal. Whether you’re building a new home or renovating an existing one, every energy-efficient feature you implement contributes to lower utility bills and a reduced carbon footprint.
Start small if needed – perhaps with improved insulation or energy-efficient windows – and gradually work your way toward more comprehensive solutions. The initial investment in energy-efficient design typically pays for itself through reduced energy costs, increased property value, and potential tax incentives.
By taking action today to create a more energy-efficient home, you’re making a positive impact that will benefit both your family and the environment for years to come. The future of sustainable living starts with the choices we make today in our home design plans.